Spartan Military Ranks - This article needs more citations for validation. Please help improve this article by adding citations from reliable sources. Unavailable items can be objected and removed. Find sources: "Military grade" - news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2016 ) (Learn how to remove this message template and what)
A poster showing the insignia of various armed forces officers during the Second World War.
Spartan Military Ranks
Intelligence agencies or other agencies organized in parallel with the military. The military rank system defines governance, authority and responsibility in the military ranks. It includes the principles of exercising power and authority in the military chain of command—the sequence of superiors to subordinates through which command is exercised. The military chain of command forms an integral part of organized joint action.
Socrates As A Soldier. Depicting The Philosopher Armed And In…
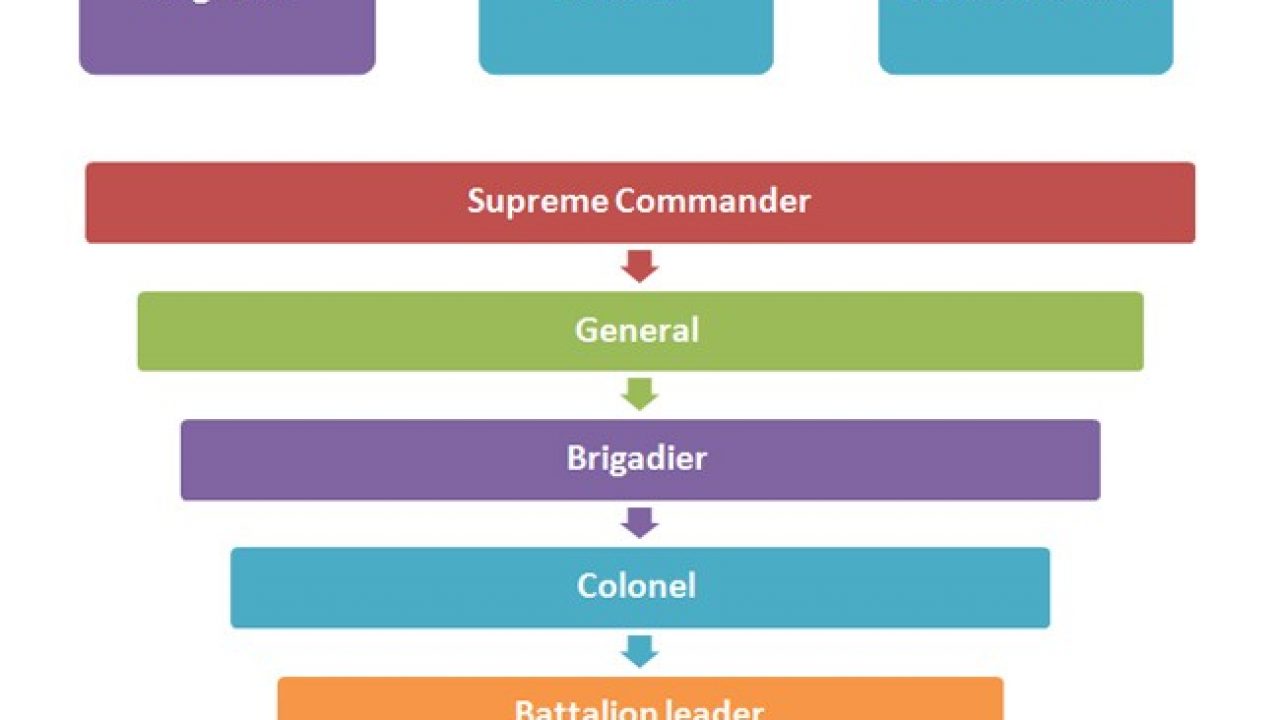
Classification systems have been known throughout much of military history to be beneficial to military operations, especially in relation to mobility, command and communication. As time and military operations became larger and more complex, military positions expanded and the classification systems themselves became more complex.
Rank is not only used to designate leadership, but also to set a standard of pay. As the rate increases, so does the rate of pay, but so does the amount of responsibility.
Within today's armed forces, the use of ranks has become almost universal. Communist states sometimes abolished ranks (eg, Soviet Red Army 1918-1935,
One of each of the "nations" established in the establishment of democracy. Sttegos means "army leader"
Ancient Greek Military Ranks Hierarchy Chart Hierarchystructure.com
And is often translated as "geral". At first these knights worked together with the old polemarchos ("warlord") but later the latter figure entered the geralship: each group would rotate as polemarch for one day, and during this day his vote would work as a group. tie-breaker if needed.
Absolute t-tests were equal to each other. There was no leadership among them, however, a basic form of democracy existed: For example, in the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC, the generals decided the battle plan by majority vote. Certain assignments, however, may be given to individual generals; inevitably there was a general division of responsibilities.
The rank below the chief officer was taxiarchos or taxiarhos, something like the modern brigadier. In Sparta, however, the title was "polemarchos". Below this was the syntagmatarchis, which can be translated as "army leader" (syntagma) and was therefore similar to the modern colonel. Below him were the tagmatarches, the officer in charge of the tagma (closer to the modern army). The position was about the size of a Roman legion. Next were the lokhagos, an officer who led a unit of infantry called izzos that covered about a hundred meters, like a modern company led by a captain.

The Greek cavalry (hippikon) was called a hipparchia and was commanded by an epihipparka. The unit was divided into two and led by two hipparchos or hipparches, but the Spartan cavalry was led by a hipparmostes. The hippotoxotès was a mounted archer. A Greek horse company was led by a tetrarchès or tetrarch.
Roman Army Enlisted Ranks Page 2 By Eliteknight248 On Deviantart
The rank and file of the military in many Greek cities was made up of ordinary citizens. The most heavily armed foot soldiers were called hoplites or hoplites and the hoplomachos were drillers or gunners.
When Aths became a naval power, the highest generals of the land forces had control over the fleet. Under them, each warship was commanded by a trièrarchos or trierarch, a term that originally meant "trireme officer" but was adopted when other types of ships came into use. In addition, as in modern naval vessels, different tasks related to running the ship were assigned to different subordinates. Specifically, the kybernètès was the charioteer, the kelustēs handled the speed of the oars, and the trièraulès was the flutist who kept pace with the oars. After further training, naval captains were replaced by nauarchos, a naval officer of the rank of admiral.
With the rise of Macedonia under Philip II of Macedonia and Alexander the Great, Greek soldiers became more professional, tactics became more sophisticated and more levels of division were developed. The infantry were organized into phalanxes of heavy infantry called phalangites. These were among the first soldiers ever to be drilled, and fought in a square, usually eight feet deep, with a leader at the head of each column (or file) and a second leader in the middle to keep the rear lines in line. move to the sides if more front is needed.
The tetrarchia was a unit of four files and the tetrarchès or tetrarch was the commander of four files; dilochia was a double file and dilochitès was a leader with two files; lochos was a single file and lochagos was the leader of the file; dimoiria was the half file and dimoirites was the leader of the half file. Another name for the hèmilochion file was hèmilochitès which was the leader of the half file.
Military Uniforms Of Ancient Greek Warriors
The different types of units, however, were different from each other and therefore their leaders had different qualifications. For example, under the counting system from ts, dekas or dekania was a unit of t headed by a dekarchos, hekatontarchia was a unit of a hundred headed by a hekatontarchos and khiliostys or khliarchia was a unit of a thousand headed by a. the chiliarchos.
The cavalry, which Alexander was most famous for (in a military sense), grew exponentially. There were units of heavy cavalry and cavalry (ilè), the latter commanded by ilarchos.
The use of official positions came into widespread use with the Roman armies after the reforms of Marius. However, the comparison with modern positions is loose because the structure of the Roman army was very different from the organization of its modern counterparts, which arose from the early modern merchant companies, of the Thirty Years' War, rather than the fourth texts. -ctur The Roman writer Vegetius and Caesar commented on his conquest of Gaul and the civil war.

The so-called military commander was a political office in Rome. It was necessary for the commander of the forces to be equipped with imperium, a political and religious concept. The king who had it (the rex sacrorum) was absolutely forbidden to have it to avoid returning to the throne. In the Republic, the administrator was limited to the consuls or (rarely) the governors, or in cases of necessity the dictator. After the establishment of the office, proconsuls were used. In imperial times, each army was commanded by a ruler, who was an ambassador or a governor.
The Victorious Gay Greek Army That Got Canceled By History
The commander can appoint a deputy, called a legate (legatus). The association of the word "legatus" with "legion" is a folk etymology, as the meaning of the word "proxy" or "voy". Legacies used to be confiscated by the Roman Empire for three years. The political nature of the high military command was evident here, as the legions were always subordinate to the emperor, and only the second legion and others stationed in the province had their own legionis. Real administrators and legates are together, in today's terms, ordinary officials.
Immediately below the commander (or his representative) were six military officers (tribuni militum), five of whom were young men of cavalry rank and one of whom was an officer who led the sate. The latter is called tribune laticlavius (tribunus laticlavius) and was second in command. If in today's divisions the deputy commander is a brigadier geral, the tribune of the laticlave may be interpreted by this rank, although he did not command any formation of his own. Some judges are called tribuni angusticlavii and are equivalent to staff officers in both ranks: major ranks, lieutenant colonel, colonel, and administrative duties. They do not command their formation. The term "military commander" is sometimes rendered in the glossary as "colonel"—most notably by the late Classicist Robert Graves in his novels Claudius and his translation of Suetonius's Twelve Caesars—to avoid confusion with political "judges of the people"; moreover, they should not be confused even with "military commanders with consular authority", which at the beginning of republican times could take the place of consuls.
The third highest military officer, in the courts of the angusticlave, was the praefectus castrorum. He, too, would have the rank of colonel in modern armies, but he was very different from the courts as his office was not part of the administrative studies, but was usually filled by former cturions. (Today's armies have a similar distinction on a lower scale—that is, between commissioned and non-commissioned officers.)
The m fighters in a legion are made up of "ranks", lines of m fight as a unit. Under the new system of Marius, the armies were divided into t cohorts (cohortes) (almost equal to battles and subordinate to the army), each consisting of three manipula, each providing 'two divisions (a small company in modern terms. ), each. covering between 60 and 160 m. Each division was led by a cturion (cturio, traditionally translated as captain), who was assisted by several officers, such as the optio. Conditions were further divided into t
Ceremony Celebrates Virginia National Guard's 414th Birthday > Virginia National Guard > News
Southern nevada health district, florida southern district court, southern district ohio bankruptcy, southern district court, federal court southern district, southern district bankruptcy, bankruptcy southern district florida, us southern district court, us attorney southern district, southern district california bankruptcy, bankruptcy southern district texas, southern district indiana bankruptcy
0 Comments